Getting Started with Programming
Options:
Blocks
OnBotJava
Android Studio
Blocks
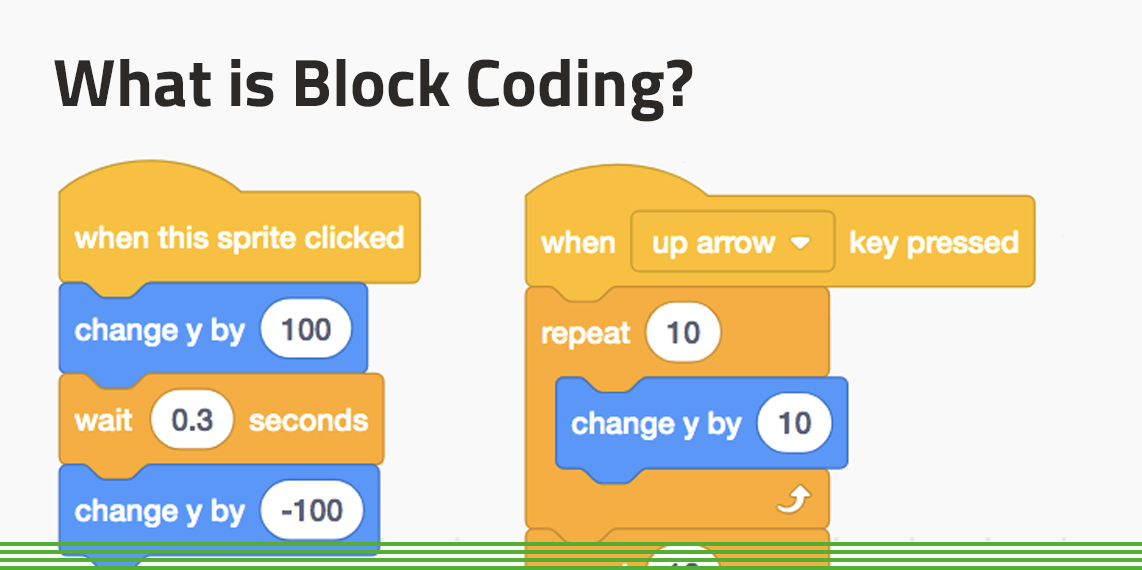
Why use blocks?
Visual programming (drag-and-drop)
Generates Java code from the blocks
No computer software required
Runs in a web browser when connected to RC
Code is stored on RC
Intended for folks who’ve never written code before
Limited usability beyond what’s available
Limited support from other teams and volunteers as many people aren’t experienced with blocks
How do I get started?
Connect to your robot via Wi-Fi or USB
Comprehensive tutorial here (read carefully): https://ftc-docs.firstinspires.org/en/latest/programming_resources/blocks/Blocks-Tutorial.html
OnBotJava
Why use it?
Much simpler to set up than Android Studio
All code is stored on the RC
No clutter of other classes
How do I start?
Connect to your robot via Wi-Fi or USB
Go to, and read through this site: https://ftc-docs.firstinspires.org/en/latest/programming_resources/onbot_java/OnBot-Java-Tutorial.html